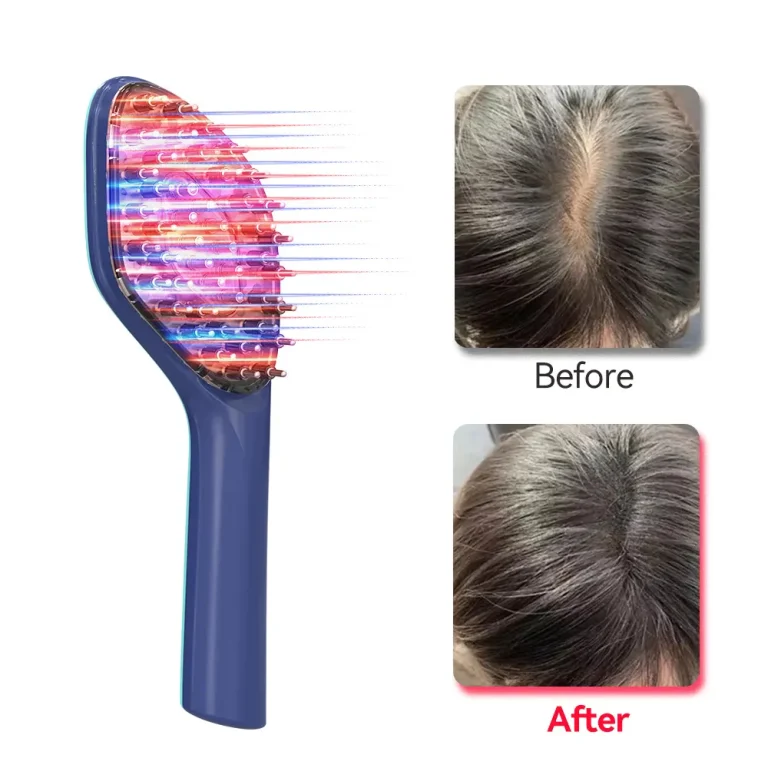
Hair loss is a common concern affecting millions of people worldwide, regardless of age or gender. While it’s normal to shed some hair daily, excessive hair loss can be distressing and impact self-esteem. Understanding the underlying causes of hair loss is the first step towards finding effective solutions. This article explores the various factors that contribute to hair loss and offers insights into potential treatments and preventive measures.
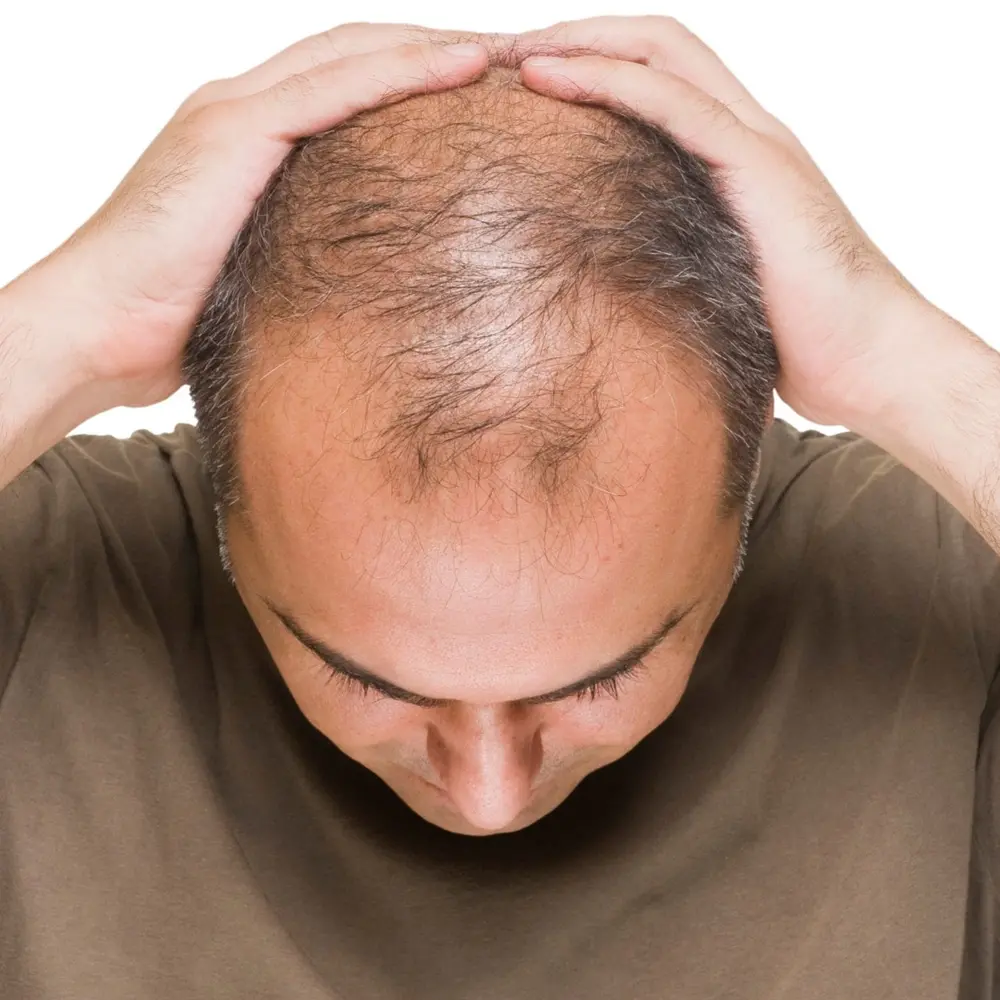

1. Genetic Factors
One of the most common causes of hair loss is genetics. Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness, is hereditary and affects a significant portion of the population.
- Male-Pattern Baldness: Typically characterized by a receding hairline and thinning at the crown. It can start as early as the teenage years and progresses over time.
- Female-Pattern Baldness: Generally involves thinning all over the scalp rather than specific bald spots. It often becomes noticeable around menopause due to hormonal changes.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating hair growth. Various conditions and life stages can cause hormonal fluctuations, leading to hair loss.
- Pregnancy and Childbirth: Many women experience hair thinning postpartum due to hormonal shifts.
- Menopause: The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause can cause hair to thin.
- Thyroid Issues: Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can lead to hair loss due to the imbalance of hormones.
3. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions and illnesses can trigger hair loss. Some of the most common include:
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss.
- Scalp Infections: Fungal infections like ringworm can cause hair to fall out.
- Lupus: An autoimmune disease that can lead to hair loss as a symptom.
4. Medications and Treatments
Several medications and medical treatments list hair loss as a potential side effect. Common culprits include:
- Chemotherapy: Targets rapidly dividing cancer cells but also affects hair follicles, leading to widespread hair loss.
- Blood Thinners: Certain anticoagulants can cause hair shedding.
- Antidepressants and Blood Pressure Medications: Some of these drugs have hair loss as a side effect.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies
A balanced diet is essential for healthy hair growth. Deficiencies in certain nutrients can lead to hair loss.
- Iron Deficiency: Often linked to hair loss, particularly in women.
- Protein Deficiency: Hair is primarily made of protein, so inadequate protein intake can affect hair growth.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Lack of essential vitamins (like Vitamin D, A, E, and B vitamins) and minerals (like zinc and selenium) can contribute to hair thinning.
6. Physical and Emotional Stress
Stress, whether physical or emotional, can significantly impact hair health.
- Physical Stress: Events like surgery, severe illness, or significant weight loss can cause temporary hair shedding, known as telogen effluvium.
- Emotional Stress: High levels of stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to increased hair loss.
7. Hair Care Practices
Certain hair care practices and styling habits can cause hair damage and loss.
- Tight Hairstyles: Styles that pull on the hair, like ponytails and braids, can lead to traction alopecia.
- Chemical Treatments: Frequent use of harsh chemicals, such as hair dyes, perms, and relaxers, can weaken hair and cause breakage.
- Heat Styling: Excessive use of heat tools like flat irons and blow dryers can damage hair and lead to thinning.
Solutions and Preventive Measures
Understanding the cause of hair loss is crucial for finding an appropriate solution. Here are some general tips and treatments:
Medical Treatments:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): Over-the-counter treatment that can help stimulate hair growth.
- Finasteride (Propecia): Prescription medication for male-pattern baldness.
- Steroid Injections: Can be effective for conditions like alopecia areata.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: A more permanent solution for significant hair loss.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes:
- Balanced Diet: Ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals.
- Stress Management: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can help reduce stress levels.
Proper Hair Care:
- Gentle Styling: Avoid tight hairstyles and harsh chemical treatments.
- Limit Heat: Minimize the use of heat styling tools and always use heat protectants.
Consult a Specialist:
If hair loss persists or is severe, consult a dermatologist or trichologist to explore potential underlying conditions and tailored treatment options.
Conclusion
Hair loss can stem from a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, medications, nutritional deficiencies, stress, and hair care practices. By understanding these causes, you can take proactive steps to address and manage hair loss effectively. Whether through lifestyle changes, medical treatments, or professional advice, there are numerous ways to combat hair loss and promote healthier hair growth.